
By @ijyoyo | Septmber 05 2020 | Envision
What is the Histogram? How can you use it for photography? A question that is asked by photographers all over the world. You probably have seen the graph in editing software such as lightroom and photoshop or on the back of your camera screen.
Learning the histogram can give you a great sense of your photo exposure and develop your photography skills!
This article will go over what the histogram does, how to use the histogram, setting the correct exposure, and avoiding clipping!
Sponsored Content
The histogram, from a dictionary standpoint, is “a diagram consisting of rectangles whose area is proportional to the frequency of a variable…”, it may be intimidating but we can break it down!
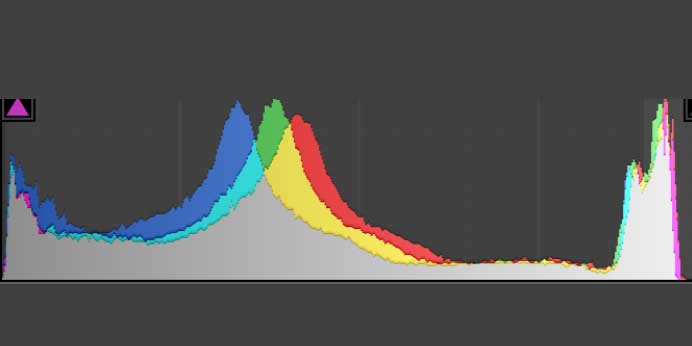
The histogram displays the light levels on the photos from the darkest parts on the left to the lightest parts on the right. You may see a histogram on your digital camera or a program. This is important to determine if the photo is well exposed across your camera LCD to computer screens and websites.
The left side is known as low-key values and the right side are high-key values. Low-key indicating shadows and high-key relating to the highlights.
The histogram can be split into different color channels. The most frequent ones are the RGB Channels, Luminosity Channel , and the CMYK Channels. These will be talked about after we see what the camera companies say about the histogram.
According to Canon using the histogram creates a combination of the aperture, shutterspeed and ISO to create a blanched image
Nikon explains how the histogram can vary between photographers and camera for the perfect exposure
And
The luminosity histogram displays information about the current light in white to black terms. You may see the Red Green Blue channels on your histogram as well or RGB channels. Let’s skip over the RGB for now.
 The luminosity histogram displays the light levels from dark on the left to light on the left. This is on a scale of 0-255. The middle of the histogram explains the 50% grey area of light.
The luminosity histogram displays the light levels from dark on the left to light on the left. This is on a scale of 0-255. The middle of the histogram explains the 50% grey area of light.
The Red, Green, Blue histogram will display the light levels against the individual color channels and the prominence of color in those areas.
The histogram displays the light levels of a photo or a live photo.
The CMYK histogram stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key. This is a standard printing color space and shouldn't be used when sharing to the web.
Now you have a general sense of what it is, how do you use it? What is a good exposure vs an under or over exposure? What is Clipping?
The first step is to figure out where it is on your camera! To find this out, put your camera name on google and search “your-camera-name histogram option”.
Once you figure that out, come back to this tutorial.
 When you are in live view or after you have taken a photo you have the ability to review your histogram.
When you are in live view or after you have taken a photo you have the ability to review your histogram.
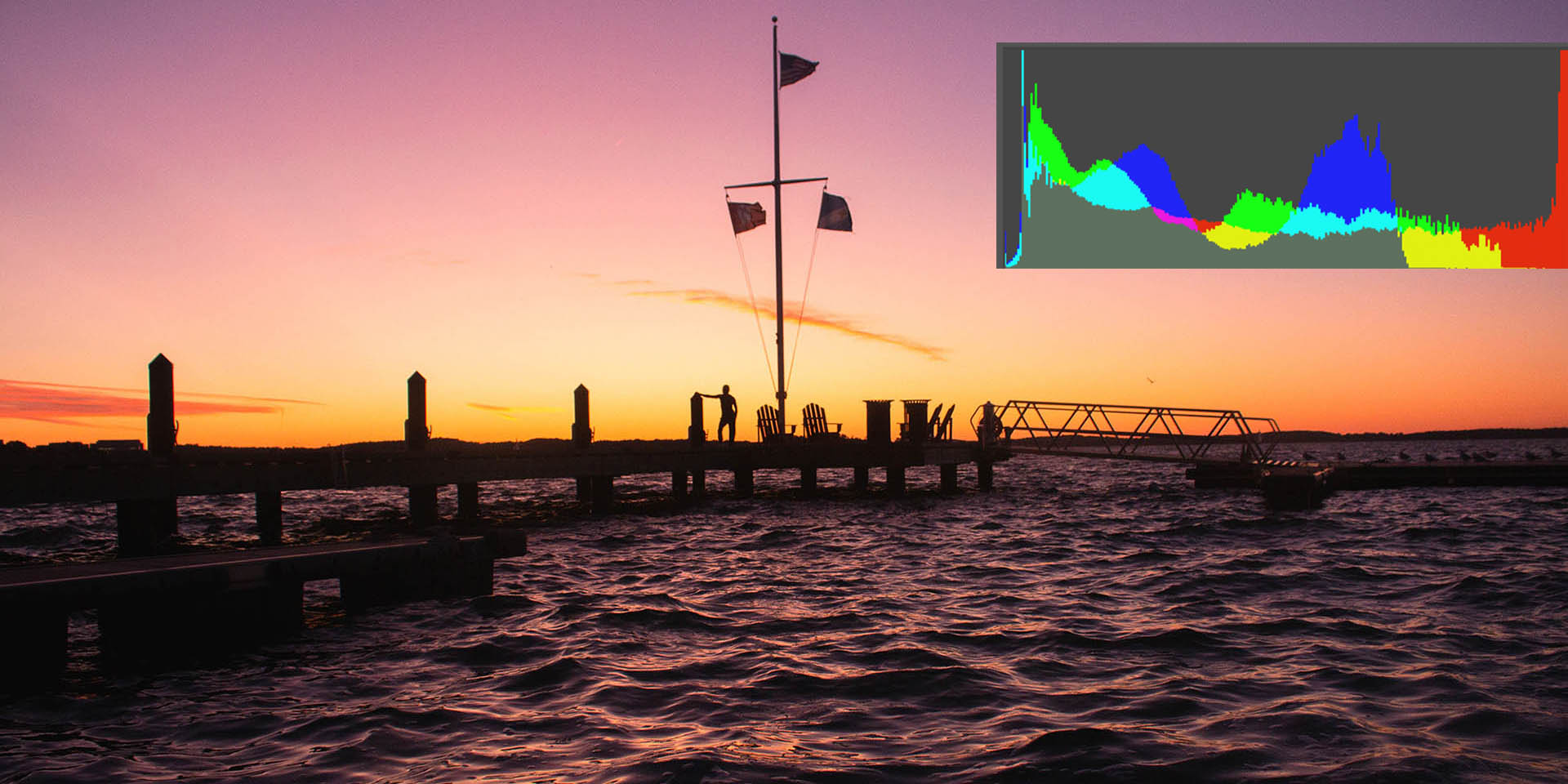
Underexposed images will skew left. And overexposed images will generally skew right. Generally a good exposure should be distrubed in the middle of the photo.

However, this is not always the case depending on your purpose for the image and the subject you are shooting. Two examples may be the classic black cat or shooting in direct sunlight photoshoots.
The first one- the black cat- will generally skew your histogram to the left with the primary focus on the blackness of the cats fur. This can misrepresent a photo, however you will lose detail if it is clipped.
This does not mean your photo is underexposed but rather that your subject matter represent the shadows more then the highlights.

The second one is if you are shooting in direct sunlight. This would skew your histogram results to the right and indicate an overexposed image. This would make sense because the sun is bright and shooting towards the sun brings more light into your image.

Clipping is where an image is right on the edge of the left or the right of the histogram. This should be avoided as much as possible on jpeg shot photos!
Clipping will lose detail in the highlights or the shadows of your image that are important for your image.
 Some modern cameras and phones have the ability to show highlights and shadow warnings, this means that there is data loss in the areas and you may want to change your exposure.
Some modern cameras and phones have the ability to show highlights and shadow warnings, this means that there is data loss in the areas and you may want to change your exposure.
Clipping can be less significant if you are shooting RAW but generally you should exposure correctly on the spot for the best results!
Using the Histogram can be great to learn and understanding how it effects exposures is important to advancing your photography skills! Also remember to avoid clipping!
The histogram is tool used in photography to evaluate an exposure from light to dark or low-key to high-key. The histogram can be used in your camera to help you create well exposed images! Make sure to avoid clippings the next time you are out, and keep creating!
